2020: The Year of QR Codes


QR codes have become incredibly popular lately, especially when it comes to making payments in the hospitality industry since the Covid-19 pandemic. But before that, they didn’t have the same level of popularity as other payment methods.
When we look at other contactless payment options like NFC or barcodes, QR codes didn’t have much presence in the Western market. People mostly saw them as a way to scan and get information, rather than a payment facilitator.
However, things have been changing recently. With the increasing adoption of QR codes, it seems like they are finally solidifying their position as a global payment method.
So, what exactly are QR codes? Well, they are digital codes that store information. Initially, they were used for tracking tool technology, but now they have evolved and are being used for various purposes in merchant services, including making payments and storing media.
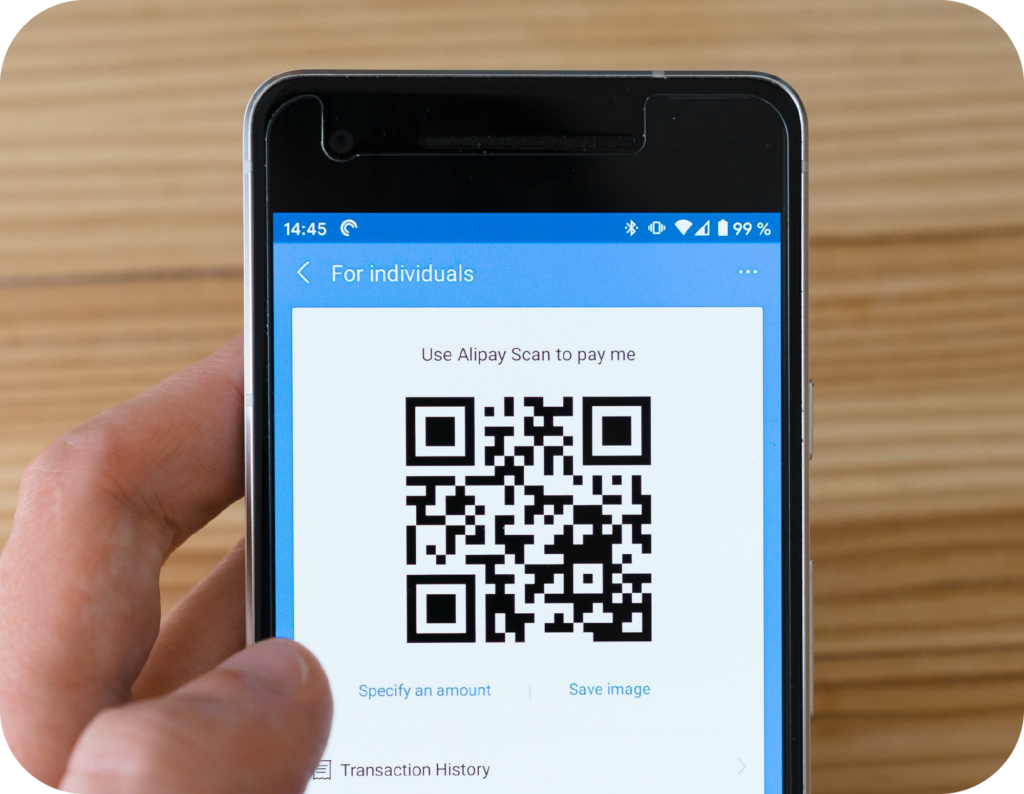
The rise in the use of QR codes has mainly been driven by their deployment in merchant payments. A good example is the popular use of QR codes in mobile payment apps like Alipay and cryptocurrency e-wallets for peer-to-peer payments. QR codes can be linked to a customer’s card or bank account, and they can either hold a preloaded value or directly debit the customer’s account.
There are several types of QR codes that you may come across:
While the technology behind NFC (near-field communication) payments is more well-known, the technology behind QR codes is less commonly understood. To make a payment with a QR code, it is facilitated by a technology called USSD (unstructured supplementary service data).
When it comes to contactless payments, NFC uses wireless communication to transfer data between devices. On the other hand, QR codes work more like SMS messages. They are essentially bundles of information compressed into those pixelated squares that you scan or present at the point of sale.
QR codes can contain up to 182 characters and can include essential and encrypted messages to facilitate communication between devices. When you scan a QR code or present it to a merchant, the information contained within the code is processed by the payment system, and the necessary transaction details are communicated between the devices involved.
The QR code credit card payment process can be described in several ways:
When we examine the data, it’s clear that QR codes have gained significant traction, particularly in certain regions.
In 2019, Alipay, one of the major players in QR code payments, had 640 million customers who regularly shopped across two or more services. Alongside its competitor, WeChat Pay, 64% of Chinese shoppers were regularly using QR codes to make payments. This highlights the popularity of this type of payment in China.
Alipay has also expanded its presence into North America, allowing QR payments through partnerships with Nayax and Yuansfer at over 100,000 self-serve locations.
Even the year before the pandemic, QR code usage in the United States had seen a 7% increase across households. However, digital payments, in general, are more prevalent in China, where they hold a 44% market share in 2020. Although Alipay’s expansion into other markets is significant, it should be noted that it primarily targets specific demographics, such as tourists in Europe.

On a global scale, when we specifically consider QR code payments, China holds a significant share at 16.4% thanks to Alipay and WeChat Pay. However, they are not the dominant leaders worldwide. Japan rivals the Chinese market with a 16% share, driven by brands like Line Pay. In the Middle East, Saudi Arabia holds a larger stake with a 24.2% share, thanks to brands like BayanPay.
While the data doesn’t clearly indicate a strong presence of QR code payments in Western markets, it is evident that QR codes have established themselves across the globe and are gradually making their way into larger Western markets like the United States. However, the pace of adoption is still a question mark.
The success of QR codes in the East can be attributed to minimal credit card usage, which reduces the need for NFC technology, and the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies. In the West, the rise of QR codes was primarily driven by hygiene and security concerns during the pandemic, as well as catering to tourist consumers.
Ultimately, the convenience and smartness of QR codes compared to existing payment methods will determine their long-term adoption. As the payments landscape rapidly adapts, QR codes have emerged as a viable option, but their full potential is yet to be realised.
The question of whether QR payments are here to stay is an interesting one, considering the rapid growth they have experienced.
According to projections, QR codes are expected to account for 10-15% of all payments worldwide by 2023, indicating a continued rise in their usage. However, the rate of adoption may vary across different countries.
Overall, the adoption of mobile payments globally is predicted to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 27% between 2020 and 2025. This growth is supported by a McKinsey report, which suggests that while traditional point-of-sale transactions may decrease, the number of contactless payments, including QR codes, is expected to increase due to the perceived sense of hygiene and security.
In Asia, QR code scanners have been widely used alongside point-of-sale systems for years. This trend is likely to continue, especially as credit adoption increases in other QR code-dominant regions, such as the Middle East. In the Western market, the future of form of payment will depend on how long consumers value the hygiene and security benefits of QR contactless payments and the overall trajectory of digital payment adoption.
Considering the growth projections and the sustained usage in certain regions, it seems that QR payments have a strong foundation and are likely to stay relevant in the payments landscape.
When it comes to contactless payments, QR codes have emerged as a significant player. In 2020, digital payments made by consumers were expected to surpass £3.2 trillion. Within that impressive figure, QR codes have made a substantial contribution. Notably, in the East, market dominance is seen through key players like Alipay and WeChat Pay. More recently, partnership schemes have helped QR codes gain momentum in the Western market as well.
The widespread adoption of QR codes as a payment method showcases their effectiveness and convenience for both consumers and merchants. As they continue to gain popularity, we can expect QR codes to play an increasingly important role in the world of contactless payments. Want to know about how you can accept QR code payments? Get in touch today!